Enter your email address to receive the latest ITVET news, market insights, and useful IT tips.
In the contemporary business landscape, cybercrime emerges as one of the most formidable threats. It now stands as the world’s third-largest economy, with the annual cost anticipated to reach a staggering $13.8 trillion by 2028. As your network, systems, and data remain vulnerable, safeguarding your business becomes crucial. In this article, we delve into the impact of cybercrime on business and the concealed costs.
What is cybercrime?
Cybercrime encompasses a spectrum of criminal activities executed through technology and the internet. Cybercriminals exploit vulnerabilities in computer systems and networks, primarily for financial gain, though motives may vary, encompassing personal or political agendas.
Irrespective of motive, the impact of cybercrime on business can be severe. Hence, investing in cyber security is paramount to shielding your business against costly malicious attacks.
What are the different types of cybercrime?

Data breaches
The number of data breaches has more than tripled between 2013 and 2022. Data breaches can cause severe reputational damage and impact your bottom line. Even accidental data breaches can put your company’s reputation at stake.
At the beginning of 2024, the ‘Mother Of All Breaches‘ (MOAB) exposed 26 billion user records from various platforms such as Twitter, Dropbox and LinkedIn. This is one of the largest data breaches of all time.
Phishing emails
Phishing is the most common type of cybercrime, accounting for 84% of all attacks. A phishing attack is an email disguised as a legitimate one that tricks you into providing private information. There are different types of phishing including spear phishing, vishing and whaling.
One in three employees will fall prey to phishing emails. It’s one of the biggest cyber threats to your business so it’s important that your team know how to tell if an email is from a scammer.
Ransomware
Ransomware is a type of malware designed to block access to your computer systems until a sum of money (ransom) has been paid. Most of the time ransomware gets into your computer through a phishing email that contains an infected attachment. You need to be wary of suspicious-looking emails and take the necessary steps to improve email security.
Fraud
There are different types of fraud, but the one that most commonly affects businesses is Business Email Compromise (BEC). This type of fraud targets employees, especially those in the finance team.
BEC is a form of phishing attack where the unsuspecting victim receives an email using a false identity, usually someone in senior management, and is tricked into transferring money to illegitimate accounts. This can be one of the most financially damaging types of phishing attacks. This reiterates the need for powerful email security to protect your business against cyber threats.
DoS attacks
The goal of a Denial-of-Service (DoS) attack is to make a machine or network unavailable to users. The attacker overwhelms the machine or network with traffic, causing it to crash. Most victims of DoS attacks are high-profile organisations such as banking, media companies and government agencies.
A DoS attack itself won’t directly result in the theft or loss of data or other assets. However, the disruption to operations can cause loss of business and reputational damage.
Who is affected by cybercrime?
Everyone is at risk of cybercrime, but some businesses are more vulnerable than others:
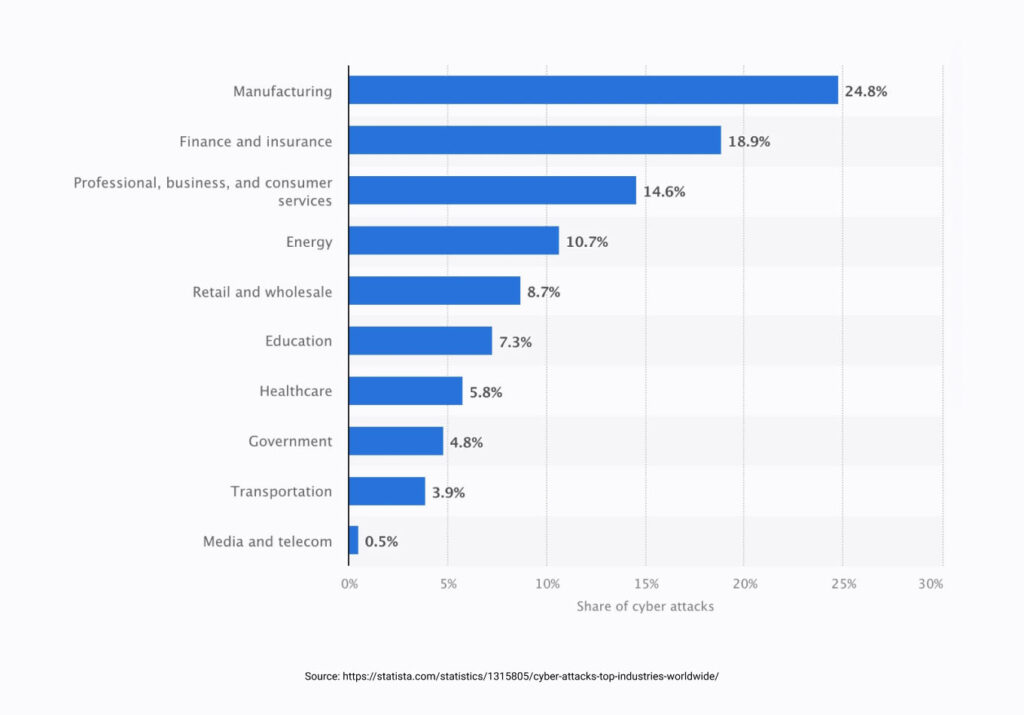
Let’s take a closer look at some of these industries:
Professional services

Professional services are a prime target for cybercriminals because they hold a large amount of confidential and sensitive information on their clients.
In April 2023, global law firm Proskauer Rose revealed that a security lapse left 184,000 client files exposed for six months. The files contained financial and legal documents, contracts, non-disclosure agreements, and data relating to high-profile mergers and acquisitions. The information had been stored by a third-party vendor on an unsecured server and was publicly accessible by anyone who knew where to look. This was likely an accidental breach, but it still damaged the company’s reputation, and if it was left unnoticed for any longer it could have been worse.
Retail

The retail industry holds a lot of financial data, including credit card numbers, making them an attractive target. Cybercriminals steal this information to commit fraud such as opening new accounts, taking out loans and making purchases in someone else’s name.
In January 2023, JD Sports was the victim of a cyberattack that leaked the personal information of 10 million customers. The information included full name, billing address, email address, phone number and last four digits from payment card numbers. This massive data breach put their customers at risk of potential scams. As a result, their customers were warned by the Information Commissioner’s Office to be vigilant.
What are the effects of cybercrime on business?
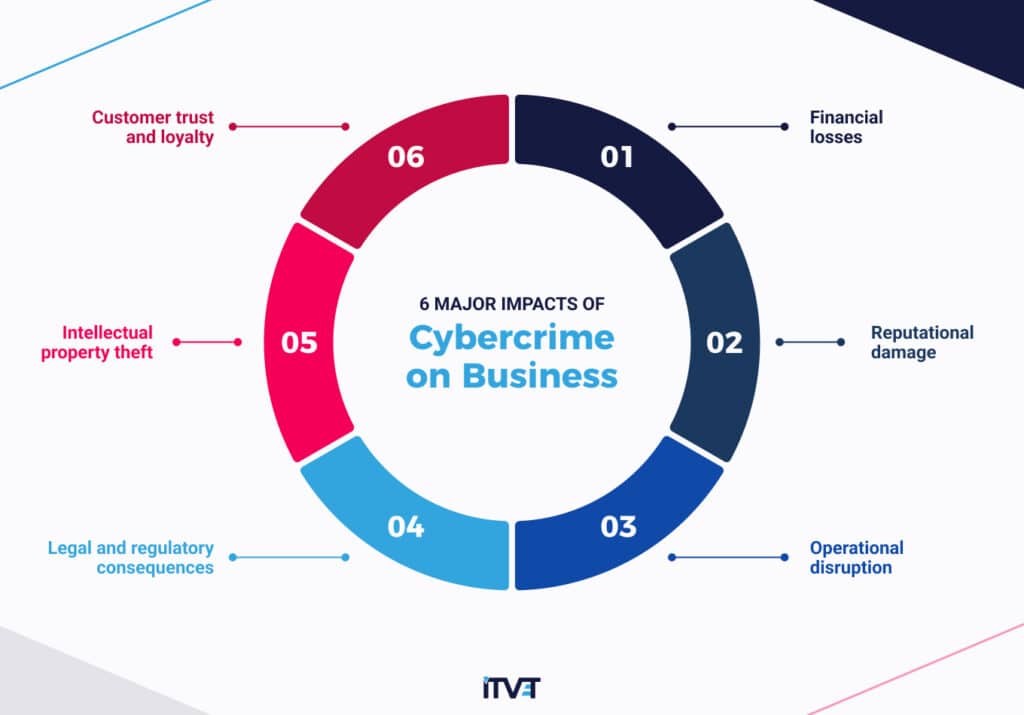
1. Financial losses
Why does cybercrime cost businesses money? Let’s look at the potential losses a business might incur:
- Recovery and remediation
After a cyberattack, companies often hire a cyber security expert to investigate and repair the damage. On top of that, they’ll strengthen the digital defences to protect the business against future attacks.
You might also need to factor in additional costs such as software licences and cyber security awareness training for employees. These expenses can quickly mount up, but the cost of a cyberattack is much higher than the cost of hiring a cyber security specialist. - Ransom payments
In the event of a ransomware attack, businesses might decide to pay the ransom to regain access to their data. Ransomware can create a huge financial burden for companies with payments stretching into the millions. In the UK the average ransomware payment in 2023 was $2.1 million, which is higher than the global average.
The official advice is not to pay ransom demands, but it depends on how desperate you are to get the data back. According to a recent survey, just over half of UK businesses have a policy against paying ransom demands. - Legal and regulatory penalties
Data breaches can land businesses in hot water and result in severe penalties and legal actions:
– Data protection and privacy laws
Businesses must comply with data protection laws and regulations or face hefty fines. For example, the UK’s GDPR can fine you up to £17.5 million or 4% of global turnover, depending on which is higher. In 2023, GDPR fines hit a record high with massive penalties against tech giants such as Meta and TikTok.
– Liability and legal actions
A company may be subject to legal action when it fails to effectively safeguard customer data. This includes Group Litigation Orders (GLO), regulatory inquiries and penalties from government authorities. For example, in 2018 British Airways faced a £500 million lawsuit when the payment card details of 420,000 customers were leaked. - Customer compensation
If customer data is compromised, businesses might be obligated to compensate customers who have been affected. This would cover any potential financial losses and the cost of identity theft protection services. - Increased insurance premiums
Cyber insurance is designed to help your business stay afloat if you’re targeted by a cyberattack. If you need to make a claim, like all insurance policies, you’ll need to pay a premium. The amount you pay depends on the cyber insurance policy.
The bad news is that the cost of cyber insurance premiums has increased significantly over the past couple of years. At the beginning of 2022, the pricing increased by 102%, largely due to a surge in ransomware attacks. - Public relations/crisis management
In response to a cyberattack, companies might seek help from a specialist Public Relations (PR) agency. The fallout from a PR crisis can be devastating, but working with a reputable PR agency can help limit the damage. How you handle public disclosure of a cyberattack can significantly affect your company’s reputation and future revenue.
Cybercrime can result in substantial financial losses for businesses. To mitigate these losses, you need to invest in a robust cyber security strategy. This should include measures such as data encryption, password management, powerful firewalls and cyber security awareness training.
2. Reputational damage
A cyberattack can erode customer trust and significantly tarnish a company’s reputation. As a result, companies might see a sudden drop in revenue. Publicly listed companies might also see a drop in market value. A report found that the share prices of companies on the New York Stock Exchange dropped by an average of 3.5% following a cyberattack.
Reputational damage is difficult to recover from. Rebuilding your company’s reputation takes time and requires considerable investment in PR and marketing efforts.
3. Operational disruption
A cyberattack can disrupt business operations, causing downtime and loss of productivity. In the worst-case scenario, your entire company could come to a standstill. These interruptions can be costly, and some businesses don’t bounce back from them.
Cyber security measures such as automated backups, regular software updates and incident response plans can help maintain business continuity.
4. Customer trust and loyalty
Cybercrime can result in the loss of customer trust and brand loyalty, leading to a decrease in customer base and revenue. Thales reported that 21% of consumers stopped using companies that suffered a data breach, and 42% of those requested their information to be deleted.
To maintain customer trust and brand loyalty, businesses must prioritise cyber security. In the event of a cyberattack, you need to be transparent and effectively communicate with customers to reassure them.
5. Intellectual property theft
Cybercriminals often target large enterprises to steal their trade secrets, patents and private information. The impact of intellectual property theft on a business can be catastrophic. It can significantly affect your competitive edge, causing a decrease in market share and profitability.
To protect intellectual property, you should:
- Implement a zero trust strategy
- Monitor networks around the clock
- Train employees on the importance of safeguarding proprietary information
6. Legal and regulatory consequences
As previously mentioned, cybercrime can result in costly legal and regulatory actions. This is why it’s important to have robust data security measures in place to safeguard customer information.
Summary
The impact of cybercrime on business can be catastrophic, from reputational damage to operational disruptions and financial losses. Failure to implement proactive cyber security measures can leave your network and systems wide open to potential attacks. If you’re worried about your business, get in touch with ITVET today. Our team of specialists can provide expert guidance on protecting your business against costly cyberattacks.







